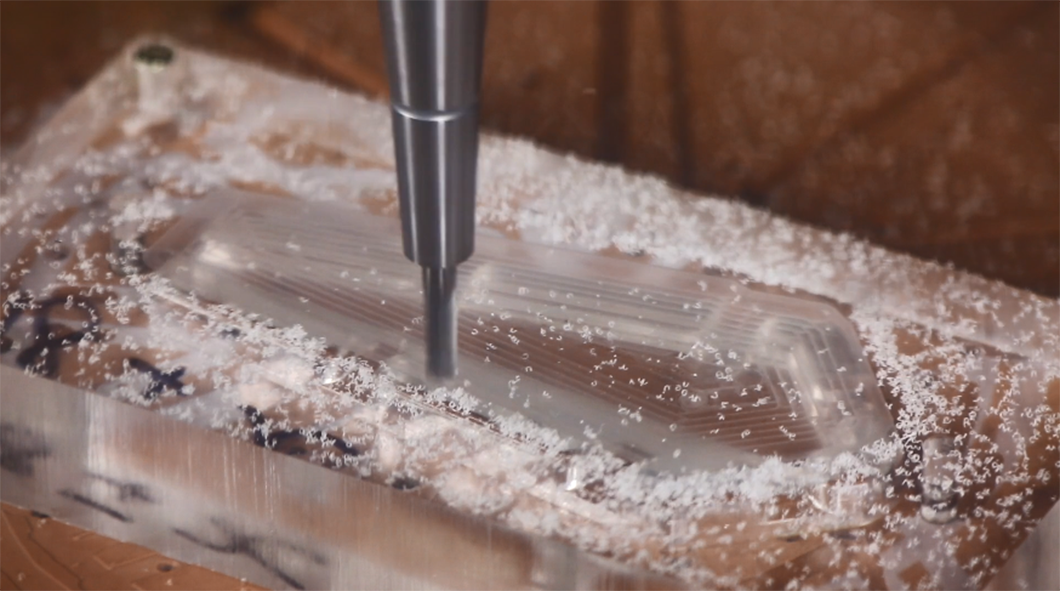
Machining consists in the precise removal of material from a block or blank to attain geometric objectives. Machining typically involves a cutting tool and controlled movement systems (computer numerical control: CNC) for the part and tool. The speeds at which the cutting operation and the part is put in movement combine to mechanically remove material chips. Computer-aided manufacturing (CAM) programs these movements (for example on 5 axes) and generate the toolpath.
CNC machinists apply CAM by selecting, measuring and preparing tools, by securing the part onto the CNC machining center, and by monitoring operations via interface software.